E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, has revolutionized the way business is conducted in the digital age. It refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet, transforming traditional commerce into a dynamic online marketplace. This article explores the concept of e-commerce, highlighting its advantages and various types.
**Definition of E-commerce:**
E-commerce encompasses a broad range of online activities, from electronic transactions and online banking to internet marketing and online shopping. At its core, e-commerce involves the exchange of products and services using electronic networks, primarily the internet.
**Benefits of E-commerce:**
1. **Global Reach:**
E-commerce breaks down geographical barriers, allowing businesses to reach a global audience. This expanded market reach opens up new opportunities for growth and customer acquisition.
2. **Convenience and Accessibility:**
One of the primary benefits of e-commerce is the convenience it offers to both businesses and consumers. With 24/7 accessibility, customers can shop anytime, anywhere, and businesses can operate without the constraints of traditional business hours.
3. **Cost Efficiency:**
E-commerce eliminates the need for physical storefronts and reduces various operational costs. This cost efficiency can translate into lower prices for consumers and higher profit margins for businesses.
4. **Data-driven Insights:**
E-commerce platforms generate a wealth of data that businesses can analyze to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions and tailor their strategies to meet customer expectations.
5. **Personalization:**
E-commerce allows businesses to personalize the shopping experience for individual customers. Through data analysis and user profiling, businesses can offer targeted promotions, product recommendations, and a more personalized customer journey.
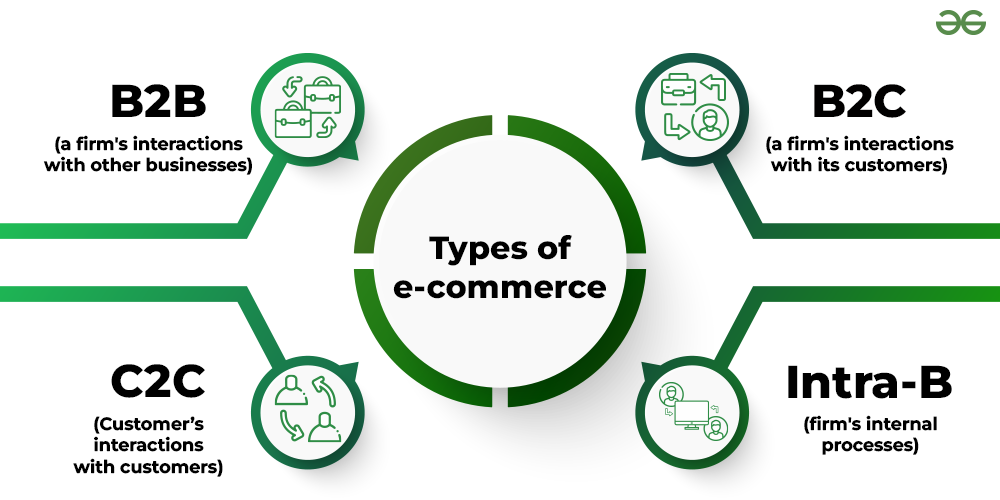
**Types of E-commerce:**
1. **B2C (Business-to-Consumer):**
In B2C e-commerce, businesses sell products or services directly to consumers. This is the most common form of e-commerce and includes online retailers, service providers, and content providers.
2. **B2B (Business-to-Business):**
B2B e-commerce involves transactions between businesses. This type of e-commerce focuses on the exchange of goods and services between different companies, such as manufacturers, wholesalers, and distributors.
3. **C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer):**
C2C e-commerce facilitates transactions between individual consumers. Online marketplaces and auction platforms are examples of C2C e-commerce, where individuals can buy and sell products directly with each other.
4. **C2B (Consumer-to-Business):**
In C2B e-commerce, individual consumers offer products or services to businesses. This can include freelancers, influencers, or individuals providing unique services that businesses are willing to pay for.
5. **B2G (Business-to-Government):**
B2G e-commerce involves transactions between businesses and government entities. This includes the provision of goods and services to government agencies.
**Conclusion:**
E-commerce has become an integral part of modern business, offering numerous benefits and diverse transactional models. Its continuous evolution and adaptability to technological advancements make it a powerful force shaping the future of commerce globally. As businesses and consumers increasingly embrace the digital landscape, the significance of e-commerce is poised to grow, driving innovation and reshaping the way we engage in commerce.







